B. Shrestha, Y. Li, A. Vertes
Metabolomics, 2008, 4, 297–311
DOI: 10.1007/s11306-008-0120-8 | Impact factor (2010): 3.871
DOWNNLOAD | ONLINE
ABSTRACT
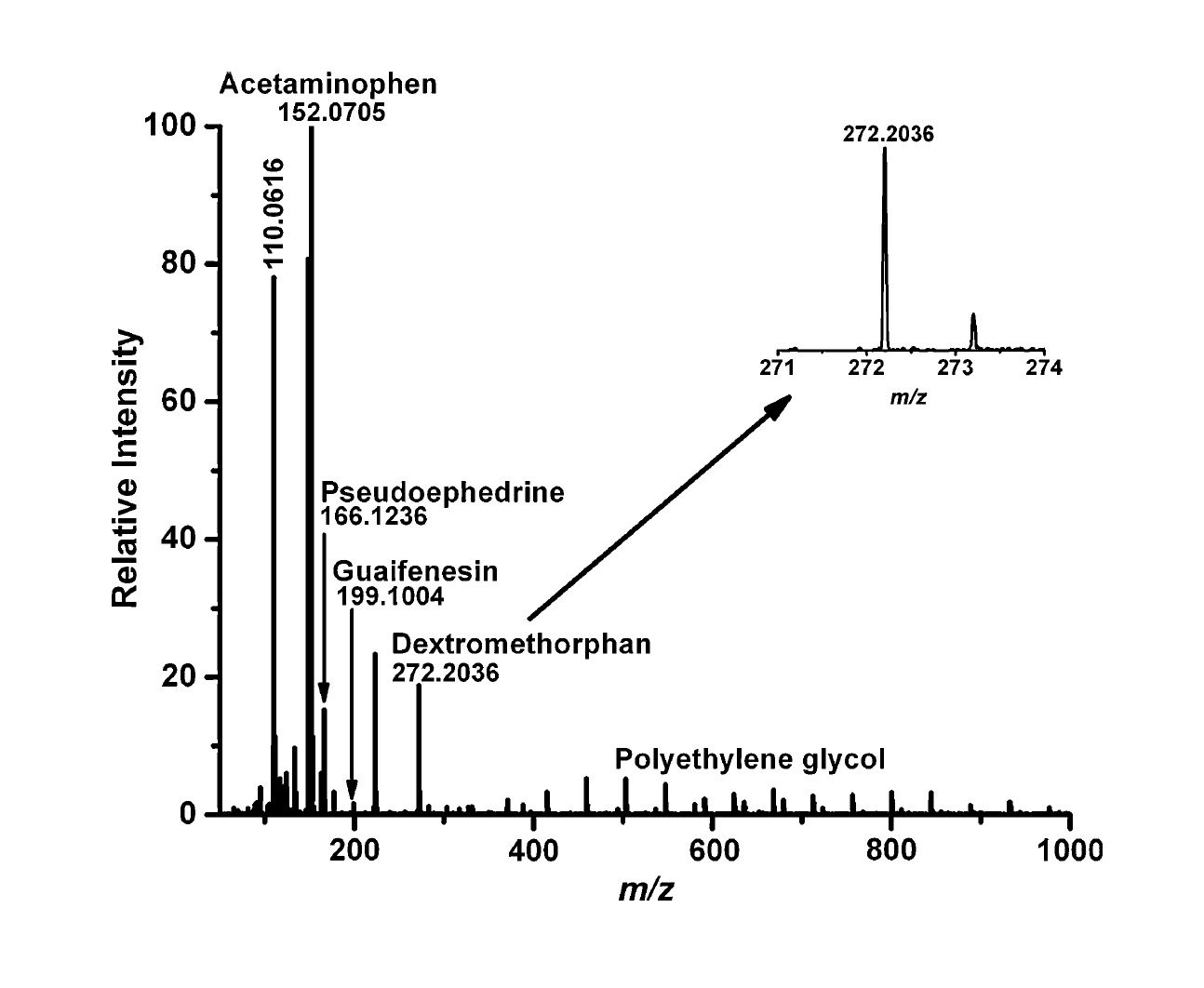
Atmospheric pressure (AP) infrared (IR) matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry (MS) was demonstrated for the rapid direct analysis of pharmaceuticals, and excreted human metabolites. More than 50 metabolites and excreted xenobiotics were directly identified in urine samples with high throughput. As the water content of the sample was serving as the matrix, AP IR-MALDI showed no background interference in the low mass range. The structure of targeted ions was elucidated from their fragmentation pattern using collision activated dissociation. The detection limit for pseudoephedrine was found to be in the sub-femtomole range and the semi-quantitative nature of the technique was tentatively demonstrated for a metabolite, fructose, by using a homologous internal standard, sucrose. A potential application of AP IR-MALDI for intestinal permeability studies was also explored using polyethylene glycol.